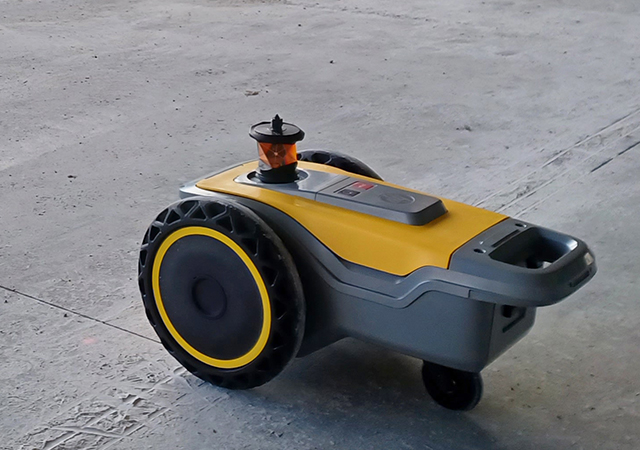
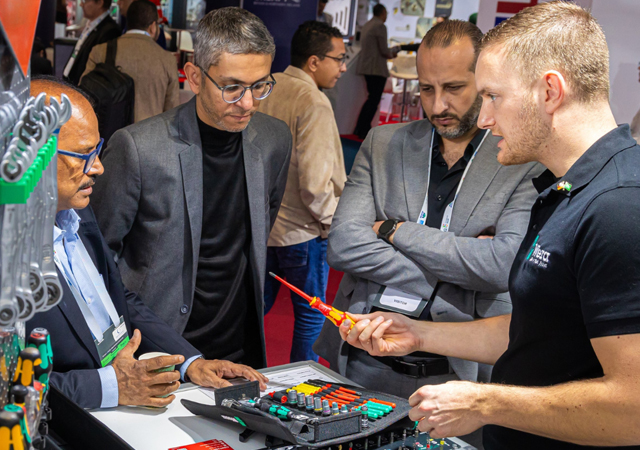
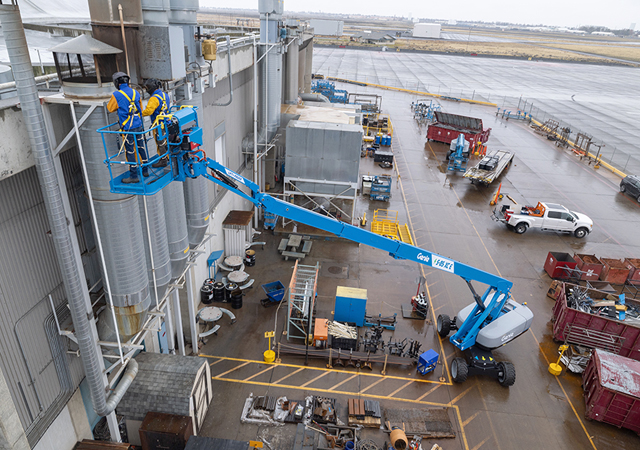
 Acciona’s HP SitePrint robot prints lines directly on the work surface.
Acciona’s HP SitePrint robot prints lines directly on the work surface.
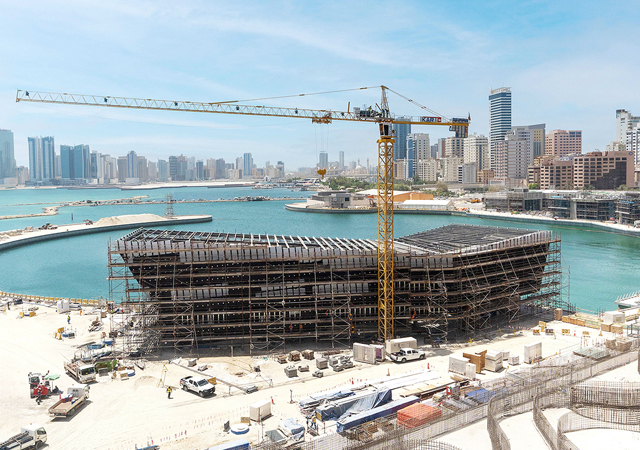
The construction industry is at the cusp of a technological transformation, driven by robotics and artificial intelligence (AI). Around the world, automated systems are reshaping the way we design, build, and manage infrastructure. Nowhere could this revolution be more impactful than in the Middle East, a region renowned for its ambitious architectural projects, rapid urbanisation, and relentless pursuit of innovation.
The Middle East is uniquely positioned to lead the adoption of robotics in construction. With billions of dollars being invested annually in infrastructure and megaprojects like Saudi Arabia’s NEOM city and the UAE’s urban expansions, the region’s construction sector is both immense in scale and ripe for modernisation. Robotics offers a transformative path to address some of the sector’s most pressing challenges: labour shortages, tight timelines, cost overruns, and safety concerns.
Leveraging tech convergence
The rise of robotics in construction has been enabled by a convergence of cutting-edge technologies: machine vision, IoT connectivity, advanced AI, and low-latency 5G networks. This convergence allows robots to perform highly specialised tasks with unprecedented efficiency and precision. For example, the SAM100 (Semi-Automated Mason) can lay hundreds of bricks per hour with unmatched accuracy, while Spot, the agile quadruped robot by Boston Dynamics, performs intricate site inspections in challenging terrains. Such innovations promise to revolutionise Middle Eastern construction sites, where scale and complexity demand technological solutions.
 |
|
Pérez |
Consider the potential of autonomous excavators and 3D printing robots. Robotic excavators equipped with GPS and LiDAR can perform earthmoving tasks with precision, reducing risks associated with heavy machinery. Similarly, 3D printing robots can produce complex structures faster and more cost-effectively, using materials like concrete and other sustainable alternatives. This technology not only enhances efficiency but also enables the creation of unique and creative architectural designs that would be difficult or costly to achieve with traditional methods. In a region where construction delays often lead to budgetary constraints, 3D printing could ensure timely and efficient project delivery while promoting innovation and sustainability in the built environment.
Addressing regional challenges
The Middle East faces unique challenges in its construction sector, such as extreme weather conditions, skilled labour shortages, and high operational costs. Robotics can mitigate these issues. For example, drones equipped with advanced sensors can monitor progress and provide real-time data, ensuring projects remain on track despite external challenges. Robots like TyBot, which automates the physically demanding task of tying rebar, can ease reliance on manual labour while improving safety and productivity.
Acciona, a Spanish multinational conglomerate dedicated to the development and management of infrastructure and renewable energy, exemplifies the transformative potential of robotics in construction, with its deployment of the HP SitePrint robot at the Alentejo Central Hospital in Évora, Portugal. As the first Spanish infrastructure company to continuously utilise this autonomous equipment, Acciona is setting a benchmark for efficiency and precision in construction design layout.
The HP SitePrint robot has enabled Acciona to significantly accelerate the layout of partition walls, achieving a pace six times faster than traditional methods.
By leveraging detailed plans entered into the robot’s operating system, it prints lines and text directly on work surfaces. Despite its advanced capabilities, the robot remains collaborative, requiring a human operator to prepare blueprints and oversee operations.
This small, wheeled mobile unit equipped with a specialised print head not only enhances accuracy but also reduces the physical burden on surveyors. At the hospital project – spanning a 140,000 sq m slab area – Acciona has successfully executed over 25,000 sq m of partition wall layouts using this technology. This showcases the robot’s effectiveness in meeting the demands of large-scale projects.
Driving sustainability, growth & innovation
The adoption of robotics aligns seamlessly with the region’s sustainability goals. Automated systems reduce material waste, optimise energy consumption, and enable eco-friendly practices like 3D-printed structures using sustainable materials. For governments prioritising green construction, such as the UAE’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, robotics offers a practical pathway to meet environmental objectives.
The integration of robotics into the construction sector also holds significant economic potential for the Middle East. By fostering a culture of innovation, governments can create new industries around robotics development, training, and maintenance. Initiatives like Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 emphasise technological advancement and economic diversification, and the robotics sector could become a cornerstone of these efforts.
Furthermore, upskilling the region’s workforce to operate and maintain advanced robotics systems can create high-quality jobs and attract global talent. Partnerships with leading robotics manufacturers and research institutions can position the Middle East as a hub for construction technology.
A future built by robots
As the Middle East continues to expand its urban landscapes and infrastructure, the adoption of robotics in construction is not just an opportunity but a necessity. By embracing these advancements, the region can build faster, safer, and more sustainably, setting a global standard for construction excellence. From towering skyscrapers to sprawling smart cities, the future of Middle Eastern architecture could well be built by robots.
It is imperative for stakeholders across the public and private sectors to collaborate in accelerating this transition. Governments must invest in research and development, create favourable regulatory environments, and incentivise the adoption of robotics. Simultaneously, construction companies should pilot these technologies, showcasing their potential to revolutionise operations. Together, they can unlock a future where innovation drives progress, cementing the Middle East’s position as a global leader in construction technology.














.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)




 Doka.jpg)






























